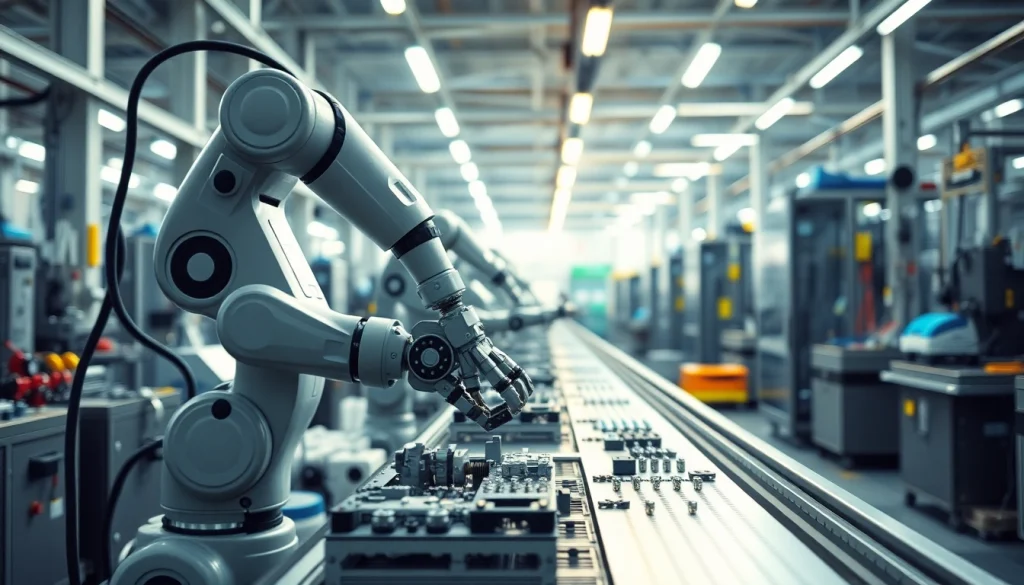
Understanding Injection Robots
What are Injection Robots?
Injection robots are automated machines designed to streamline the injection molding process in manufacturing. These robots are often utilized in industries such as plastics, automotive, medical devices, and consumer goods. They automate the tasks of loading raw materials into the injection molding machinery, removing molded parts, and sometimes even assembling components post-molding. By integrating robotics into the injection molding process, manufacturers can achieve higher levels of efficiency, reduce labor costs, and enhance product quality. Injection Robot technology continues to evolve, making it an essential tool in modern manufacturing environments.
How Injection Robots Function
Injection robots operate through a series of programmed commands that direct their movements and tasks. The typical workflow begins with the robot receiving a signal from the injection machine indicating that the molding process is complete. The robot then performs the following functions:
- Material Loading: The robot can transfer pellets or granules into the injection molding machine’s hopper, ensuring a continuous supply of material.
- Mold Opening and Closing: Robots may assist in the opening and closing of molds, ensuring tight seal integrity and efficient cycle times.
- Part Removal: Once the mold has cooled and solidified, the robot deftly removes the finished parts. This task is critical as it minimizes cycle time and prevents damage to fragile molded items.
- Quality Inspection: Advanced models are equipped with sensors that can perform inline inspections to check for defects immediately after the molding process.
These systems can be programmed for various tasks, allowing for quick adaptation to different production needs, making them highly versatile in dynamic manufacturing settings.
Applications in Various Industries
The versatility of injection robots allows for their integration across numerous industries:
- Automotive: In the automotive industry, injection robots are essential for producing parts such as dashboards, bumpers, and other plastic components efficiently and consistently.
- Consumer Products: Many household items, from containers to toys, benefit from the precision and speed of injection robots during mass production.
- Medical Devices: The healthcare sector utilizes these robots to manufacture high-durability, sterile components, ensuring compliance with strict regulatory requirements.
- Electronics: Injection robots play a crucial role in the production of enclosures and other electronic components, enhancing both quality and throughput.
By understanding the specific needs of each industry, manufacturers can tailor their use of injection robots to maximize efficiency and effectiveness.
Benefits of Implementing Injection Robots
Improved Productivity & Efficiency
One of the primary advantages of implementing injection robots is the significant enhancement of productivity. These robots can operate continuously without fatigue, enabling them to run cycles much faster than human laborers. Additionally, their precision limits the number of production errors, thereby reducing waste and scrap rates. This efficiency leads to shorter lead times and increased production volumes, helping manufacturers meet growing demands in an increasingly competitive market.
Cost Savings on Labor
While the initial investment in injection robots can seem steep, the long-term savings on labor costs are considerable. Robots reduce the need for manual labor in repetitive tasks, allowing companies to redirect workforce resources to more specialized roles that add greater value. Furthermore, robots mitigate the risks of labor costs rising due to market conditions or workforce shortages, creating a more stable operational environment.
Enhanced Precision in Manufacturing
Robots excel in precision, making them invaluable in manufacturing processes where quality is paramount. They minimize discrepancies in part dimensions, ensuring each product meets specifications. This precision is particularly important in industries such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing, where even the slightest error could have significant consequences. By improving uniformity in production, companies can enhance their brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
Choosing the Right Injection Robot
Key Features to Consider
When selecting an injection robot, several key features should inform your decision-making process:
- Payload Capacity: Consider the weight of the parts you need to handle. Ensure the robot’s payload capacity is adequate for your production needs.
- Speed: Evaluate the speed of the robot in relation to your cycle times. A faster robot can significantly reduce overall production time.
- Range of Motion: Assess the robot’s reach and degrees of freedom to ensure it can maneuver as needed within your production setup.
- Integration Capabilities: Ensure compatibility with existing systems, whether it’s the injection molding machine, quality control systems, or data analytics tools.
Comparing Different Models
With numerous models available, it’s vital to compare features and specifications across different manufacturers. Consider evaluating models from major brands based on:
- Performance ratings in similar applications
- User reviews and testimonials
- Technical support and warranty offers
- Customization options
Visiting trade shows or technology expos can provide a hands-on opportunity to assess different models and understand their operational strengths and weaknesses.
Budgeting for Your Investment
Budgeting for an injection robot involves considering both direct and indirect costs. While the purchase price is a significant factor, additional costs, such as installation, training, maintenance, and software licensing, must also be accounted for. Conducting a cost-benefit analysis can clarify potential long-term savings versus initial investments. Consider the following budgeting strategies:
- Leverage financing options offered by manufacturers or third-party lenders.
- Factor in possible increased production revenues as a direct result of enhanced efficiency.
- Investigate state or federal grants for manufacturing automation initiatives.
A comprehensive budgeting approach ensures your organization is financially prepared to adopt and sustain this technology.
Best Practices for Operating Injection Robots
Safety Protocols and Training
The operation of injection robots necessitates robust safety protocols to protect human operators and minimize risks associated with automation. Comprehensive training programs should be established to educate staff on the operational features, safety practices, and emergency procedures associated with the robots. Key safety protocols may include:
- Regular safety drills to prepare operators for emergencies.
- Clear signage around robotic work areas to warn of potential hazards.
- Establishing safety zones where human presence is restricted during robotic operations.
Regular Maintenance for Optimal Performance
Maintenance is critical in sustaining the performance of injection robots. A scheduled maintenance plan can significantly reduce downtime and extend the lifespan of the equipment. Important maintenance practices include:
- Routine inspections of all mechanical and electrical components to prevent failures.
- Calibration of precision tools to ensure consistent quality in production.
- Software updates to maintain operational efficiency and security.
Utilizing predictive maintenance tools equipped with IoT technology can further enhance maintenance practices by preemptively indicating when repairs are necessary before failures occur.
Integrating Human Operators
While injection robots enhance efficiency, it’s essential to maintain a harmonious integration between human operators and robotic systems. Humans play crucial roles in supervision, quality control, and troubleshooting. Establishing clear guidelines on the interaction between humans and machines can help enhance safety and productivity. Some best practices include:
- Designing workflows that clearly delineate between automated tasks and those requiring human oversight.
- Encouraging operators to provide feedback on robotic performance to identify areas for improvement.
- Creating a culture of collaboration and continuous learning among staff.
This integrated approach ensures that the advantages of robotic automation are complemented by human oversight and expertise.
Future Trends in Injection Robotics
Advancements in AI and Automation
The future of injection robotics is heavily influenced by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and automation. Increased intelligence in robotic systems enables more sophisticated decision-making capabilities, improving the adaptability of robots to changing production demands. Machine learning algorithms are expected to enhance operational efficiencies further by optimizing production processes based on historical performance data. As robots become more intelligent, the potential for fully autonomous factories becomes more feasible, with robots making real-time adjustments in workflow with minimal human intervention.
Potential Market Growth Insights
The global market for injection robots is expected to experience substantial growth driven by the rising demand for automation across industries. According to industry research, the market is poised for rapid expansion, fueled by factors such as labor shortages, the need for increased production efficiencies, and the ongoing evolution of advanced manufacturing processes. Companies adopting these technologies now will likely have a competitive edge, positioning themselves strategically as the market expands.
Emerging Applications and Innovations
As technology continues to evolve, so too do the applications for injection robots. Emerging innovations in areas like collaborative robotics (cobots) allow robots to work alongside humans safely, enabling even greater flexibility in manufacturing settings. Additionally, integrated robots that feature advanced 3D printing capabilities are beginning to reshape the landscape of injection molding by allowing for on-demand production of complex parts that traditional methods cannot easily achieve. Full-scale digital transformation in manufacturing processes will see further integration of data analytics, AI, and robotics, making injection robots central to the factories of the future.